Abstract
Objectives
As we analyze the incidence and the risk factor for proximal junctional problem after surgical treatment of lumbar degenerative sagittal imbalance, we want to contribute to reducing the junctional problem of surgical treatment of lumbar degenerative sagittal imbalance.
Summary of Literature Review
Surgical treatment of degenerative spinal deformity has increased. Rigid fixation was a risk factor for degenerative change of adjacent segment and failure, and it remains a big challenge for the junctional problem of surgical treatment. However, research on the correlation with risk factors is rare.
Materials and Methods
Forty four patients (mean age 66.5; range, 50-74) who had surgery due to lumbar degenerative sagittal imbalance were evaluated by the risk factor associated with junctional problems from January, 2005 to December, 2011. The risk factors were analyzed by surgical factor (proximal fusion level, using iliac screw, correction or undercorrection of lumbar lordosis compared with pelvic incidence) and patient factor (age, bone marrow density, body mass index).
Results
Junctional problems occurred in 18 patients (41%) out of 44 patients. Among these problems, there were 10 cases of fractures, 8 cases of junctional kyphosis, and 4 cases of proximal screw pull out. Among the risk factors, only the correction or undercorrection of lumbar lordosis compared with pelvic incidence in surgical factor was statistically significant. Other surgical factors and patient factors were not statistically significant.
Conclusions
Junctional problems after a surgical treatment of lumbar degenerative sagittal imbalance were common. However, we could not know the exact risk factor of junctional problems except the degree of correction of lumbar lordosis compared with pelvic incidence, because most of the risk factors were not statistically significant. So, further evaluations of the risk factor of lumbar degenerative sagittal imbalance are required.
REFERENCES
1. During J, Goudfrooij H, Keessen W, Beeker TW, Crowe A. Toward standards for posture. Postural characteristics of the lower back system in normal and pathologic conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985; 10:83–7.
2. La CE. Osteotomy of the lumbar spine for correction of kyphosis in a case of ankylosing spondylarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1946; 28:851–8.
3. Thomasen E. Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. 142–52.

4. Jimbo S, Kobayashi T, Aono K, Atsuta Y, Matsuno T. Epidemiology of degenerative lumbar scoliosis: a community-based cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37:1763–70.
5. Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, et al. Adult scoliosis: prevalence, SF-36, and nutritional parameters in an elderly vol-unteer population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:1082–5.

6. West JL 3rd, Bradford DS, Ogilvie JW. Results of spinal arthrodesis with pedicle screw-plate fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:1179–84.

7. Glattes RC, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Kim YJ, Rinella A, Edwards C 2nd. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity following long instrumented posterior spinal fusion: incidence, outcomes, and risk factor analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:1643–9.
8. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Glattes CR, Rhim S, Cheh G. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity after segmental posterior spinal instrumentation and fusion: minimum five-year followup. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:2179–84.
9. Hostin R, McCarthy I, O'Brien M, et al. Incidence, Mode, and Location of Acute Proximal Junctional Failures Following Surgical Treatment for Adult Spinal Deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:1008–15.
10. Yagi M, Akilah KB, Boachie-Adjei O. Incidence, risk factors and classification of proximal junctional kyphosis: surgical outcomes review of adult idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:E60–8.
11. Wood KB, Schendel MJ, Ogilvie JW, Braun J, Major MC, Malcom JR. Effect of sacral and iliac instrumentation on strains in the pelvis. A biomechanical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:1185–91.
12. Erickson MA, Oliver T, Baldini T, Bach J. Biomechanical assessment of conventional unit rod fixation versus a unit rod pedicle screw construct: a human cadaver study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:1314–9.
13. Jackson RP, McManus AC. Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:1611–8.
14. Etebar S, Cahill DW. Risk factors for adjacent-segment failure following lumbar fixation with rigid instrumentation for degenerative instability. J Neurosurg. 1999; 90:163–9.

15. Watanabe K, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Kim YJ, Koester L, Hensley M. Proximal junctional vertebral fracture in adults after spinal deformity surgery using pedicle screw con-structs: analysis of morphological features. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:138–45.
16. Toyone T, Ozawa T, Kamikawa K, et al. Subsequent vertebral fractures following spinal fusion surgery for degenerative lumbar disease: a mean ten-year followup. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:1915–8.
17. Kumar MN, Baklanov A, Chopin D. Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur Spine J. 2001; 10:314–9.

18. Schwab F, Lafage V, Patel A, Farcy JP. Sagittal plane considerations and the pelvis in the adult patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:1828–33.

19. Cole TC, Burkhardt D, Ghosh P, Ryan M, Taylor T. Effects of spinal fusion on the proteoglycans of the canine intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res. 1985; 3:277–91.
20. Kahanovitz N, Arnoczky SP, Levine DB, Otis JP. The effects of internal fixation on the articular cartilage of un-fused canine facet joint cartilage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1984; 9:268–72.

21. Lee CK, Langrana NA. Lumbosacral spinal fusion. A biomechanical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1984; 9:574–81.

22. Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Widell EH, et al. A biomechanical study of intrapeduncular screw fixation in the lumbosacral spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 99–112.

23. Halvorson TL, Kelley LA, Thomas KA, Whitecloud TS 3rd, Cook SD. Effects of bone mineral density on pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:2415–20.

24. Meredith DS, Schreiber JJ, Taher F, Cammisa FP Jr., Girardi FP. Lower preoperative hounsfield unit measurements are associated with adjacent segment fracture after spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:415–8.

Figures and Tables%
Fig. 1.
The schema displays he cobb's method of thoracic kyphosis, thoracolumbar kyphosis, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal vertical axis. Pelvic parameter (pelvic tilt, sacral slope, and pelvic incidence) is also on lateral whole spine. TK, thoracic kyphosis; TLK, thoracolumbar kyphosis; LL, lumbar lordosis; SS, sacral slope; PT, pelvic tilt; PI, pelvic incidence; SVA, sagittal vertical axis
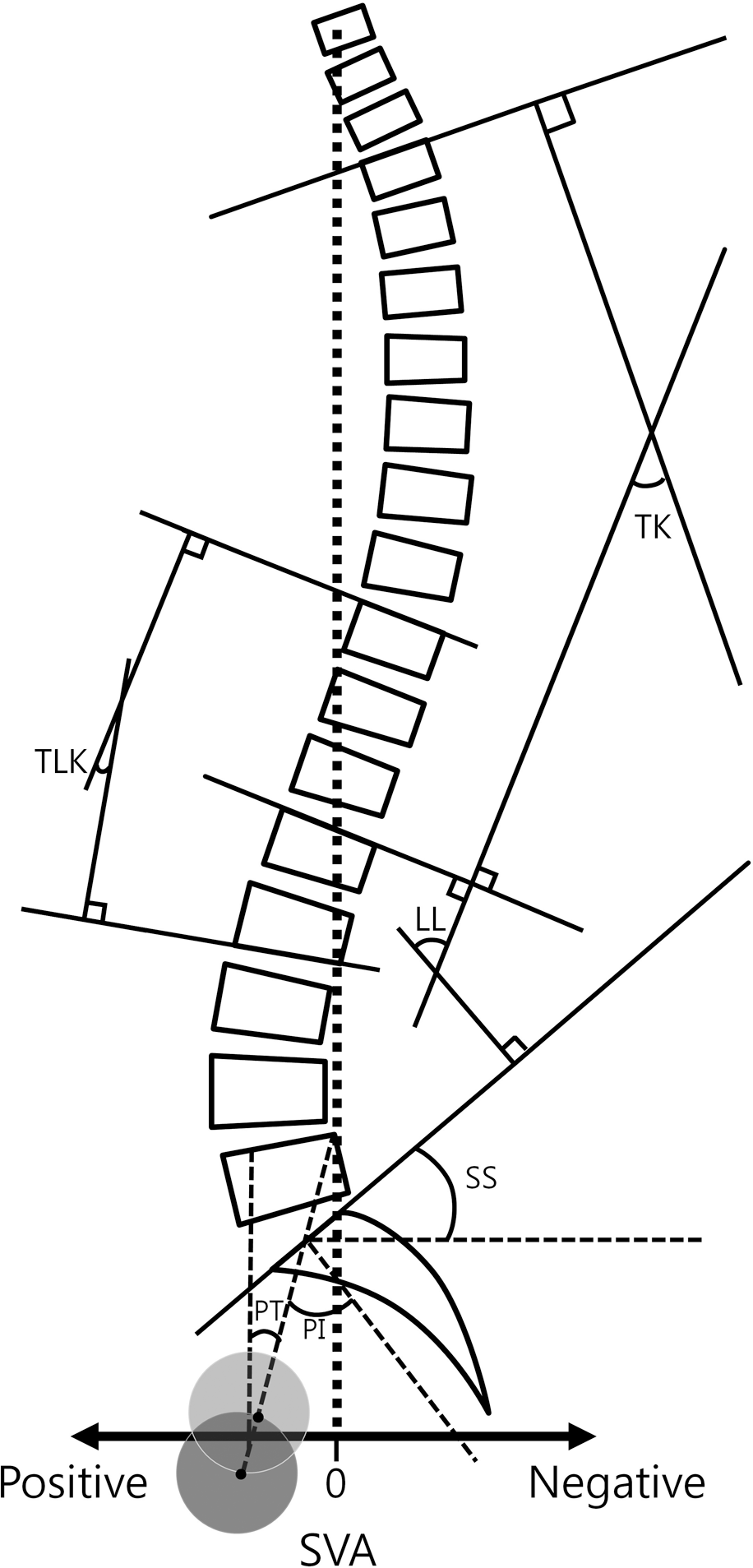
Fig. 2.
(A) A 64-year-old woman has lumbar degenerative sagittal imbalance with kyphosis. (B) She underwent an operation of L3 TPV, T12-S1 PLF. The whole spine lateral radiograph shows restored sagittal balance immediate postoperative period. (C) Junctional kyphosis with proximal screw loosening had been developed 76 months after surgery. (D) The patient had revision surgery of T10-12 PF with rod change and lumbosacral fixation with iliac screw.
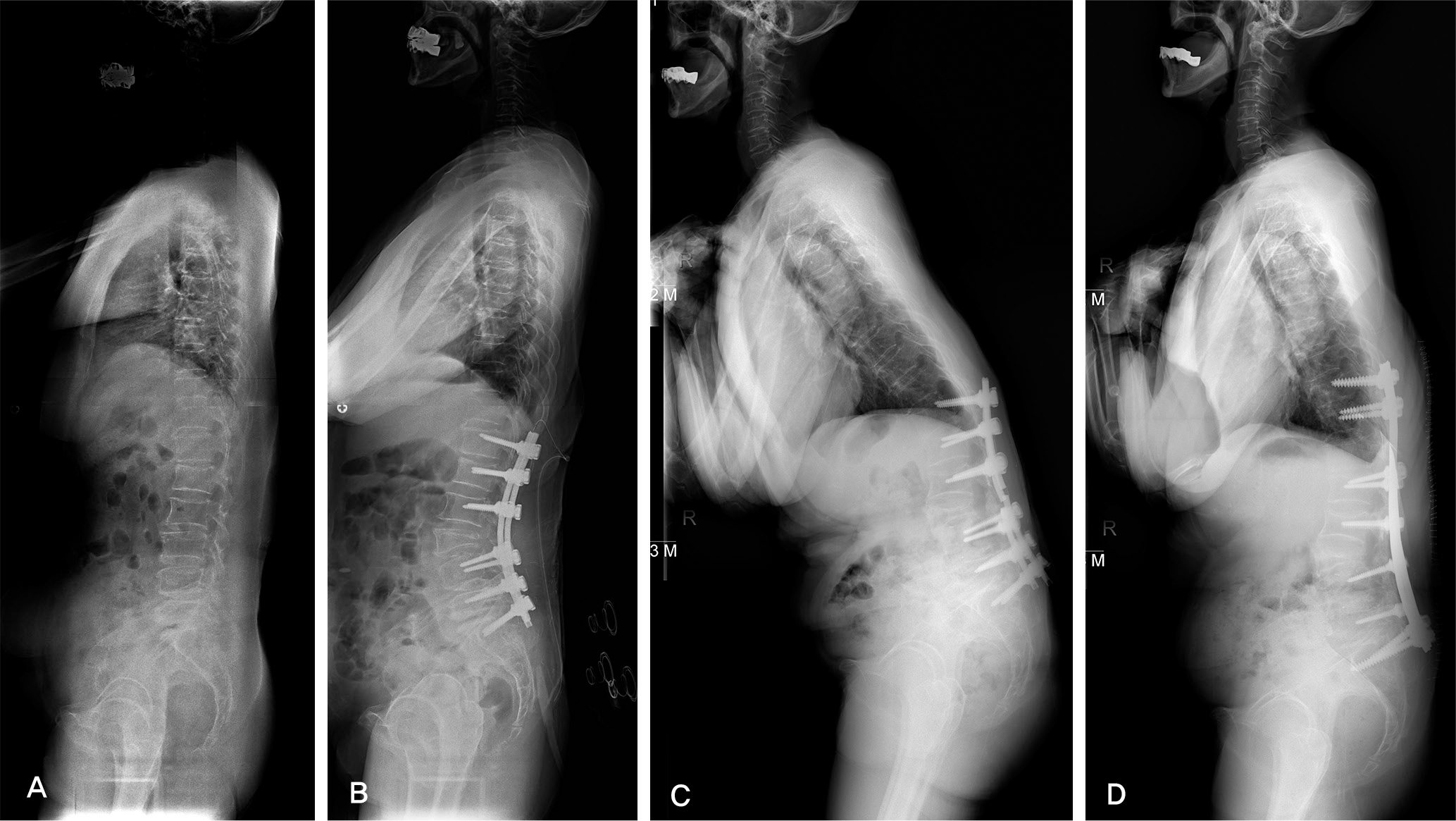
Table 1.
Average results of radiographic index for perioperative period
Table 2.
Assessment of surgical factors as a related factor for proximal junctional problem




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download