Abstract
Background:
We investigated hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection cases, who were HBsAg negative by radioimmunoassay (RIA) and HBV DNA positive for their clinical characteristics, the S gene mutation of hepatitis B virus (HBV), and usefulness of other HBsAg immunoassay.
Methods:
Among the patients requested for HBV DNA quantification, 16 patients positive in HBV DNA but negative in HBsAg RIA (BNIBT HBsAg Kit, China) were enrolled. The “a” determinant of HBV S gene was sequenced and clinical characteristics were reviewed. Additional HBsAg assay was performed using Architect HBsAg kit (Abbott laboratories, USA) employing chemiluminescent immunoassay method.
Results:
Eleven of the 16 patients showed multiple mutations in the “a” determinant. These patients received liver transplantation several years ago and have been treated with hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) and antiviral drugs. G145R mutation was found in 8 patients and G145K, D144G, and D144A were also frequently found. Among 9 of the 11 patients tested for HBsAg by Architect HBsAg kit, 8 showed positive results. Among 4 of the remaining 5 patients, only 2 showed weak positive results (≤1 IU/mL) in Architect HBsAg kit.
Conclusions:
HBV DNA-positive/HBsAg RIA-negative results were mostly observed in the patients treated with HBIG after liver transplantation, in whom HBIG escape mutations were found. Majority of these cases were positive in Architect HBsAg assay, and it is recommended to use other HBsAg immunoassay methods that are more sensitive than RIA in the detection limit as well as in the detection of escape mutant in hospitals performing liver transplantation.
REFERENCES
1.Raimondo G., Pollicino T., Cacciola I., Squadrito G. Occult hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2007. 46:160–70.

2.Carreno V., Bartolome J., Castillo I., Quiroga JA. Occult hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections. Rev Med Virol. 2008. 18:139–57.
3.Hollinger FB. Hepatitis B virus infection and transfusion medicine: science and the occult. Transfusion. 2008. 48:1001–26.

4.Coleman PF., Chen YC., Mushahwar IK. Immunoassay detection of hepatitis B surface antigen mutants. J Med Virol. 1999. 59:19–24.

5.La'ulu SL., Roberts WL. The analytic sensitivity and mutant detection capability of six hepatitis B surface antigen assays. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006. 125:748–51.
6.Cha CH., Sohn YH., Jang S., Lee HJ., Lee KJ., Shin ES, et al. Genotype analysis of hepatitis B virus isolated from Korean hepatitis patients. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:352–6. (차충환, 손용학, 장성수, 이한주, 이관제, 신은순, 오흥범. 국내 환자에서 분리된B형 간염바이러스의 유전자형 분석. 대한진단검사의학회지 2003;23:352-6.).
7.Soldan K., Ramsay M., Collins M. Acute hepatitis B infection associated with blood transfusion in England and Wales, 1991-7: review of database. BMJ. 1999. 318:95.

8.Liu CJ., Lo SC., Kao JH., Tseng PT., Lai MY., Ni YH, et al. Transmission of occult hepatitis B virus by transfusion to adult and pediatric recipients in Taiwan. J Hepatol. 2006. 44:39–46.

9.Saraswat S., Banerjee K., Chaudhury N., Mahant T., Khandekar P., Gupta RK, et al. Post-transfusion hepatitis type B following multiple transfusions of HBsAg-negative blood. J Hepatol. 1996. 25:639–43.

10.Satake M., Taira R., Yugi H., Hino S., Kanemitsu K., Ikeda H, et al. Infectivity of blood components with low hepatitis B virus DNA levels identified in a lookback program. Transfusion. 2007. 47:1197–205.
11.Weber B. Genetic variability of the S gene of hepatitis B virus: clinical and diagnostic impact. J Clin Virol. 2005. 32:102–12.

12.Carman WF., Trautwein C., van Deursen FJ., Colman K., Dornan E., McIntyre G, et al. Hepatitis B virus envelope variation after transplantation with and without hepatitis B immune globulin prophylaxis. Hepatology. 1996. 24:489–93.

13.Terrault NA., Zhou S., McCory RW., Pruett TL., Lake JR., Roberts JP, et al. Incidence and clinical consequences of surface and polymerase gene mutations in liver transplant recipients on hepatitis B immunoglobulin. Hepatology. 1998. 28:555–61.

14.Cooreman MP., Leroux-Roels G., Paulij WP. Vaccine- and hepatitis B immune globulin-induced escape mutations of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J Biomed Sci. 2001. 8:237–47.

15.Zanetti AR., Tanzi E., Manzillo G., Maio G., Sbreglia C., Caporaso N, et al. Hepatitis B variant in Europe. Lancet. 1988. 2:1132–3.

16.Carman WF., Zanetti AR., Karayiannis P., Waters J., Manzillo G., Tanzi E, et al. Vaccine-induced escape mutant of hepatitis B virus. Lancet. 1990. 336:325–9.

17.Oon CJ., Chen WN., Goo KS., Goh KT. Intra-familial evidence of horizontal transmission of hepatitis B virus surface antigen mutant G145-R. J Infect. 2000. 41:260–4.

18.Chakravarty R., Neogi M., Roychowdhury S., Panda CK. Presence of hepatitis B surface antigen mutant G145R DNA in the peripheral blood leukocytes of the family members of an asymptomatic carrier and evidence of its horizontal transmission. Virus Res. 2002. 90:133–41.

19.Song BC., Kim SH., Kim H., Ying YH., Kim HJ., Kim YJ, et al. Prevalence of naturally occurring surface antigen variants of hepatitis B virus in Korean patients infected chronically. J Med Virol. 2005. 76:194–202.

20.Hsu CW., Yeh CT., Chang ML., Liaw YF. Identification of a hepatitis B virus S gene mutant in lamivudine-treated patients experiencing HBsAg seroclearance. Gastroenterology. 2007. 132:543–50.

21.Lee SY., Choi MS., Lee D., Lee JH., Koh KC., Paik SW, et al. Overlapping gene mutations of hepatitis B virus in a chronic hepatitis B patient with hepatitis B surface antigen loss during lamivudine therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:433–7.

Fig. 1.
Amino acid sequences of major hydrophilic region (100-160) including “a” determinant (124-147) in HBV S gene of 16 patients. Lower cases mean that its amino acids are mixed with reference amino acids. “∗” shown in pt 15 indicates that its sequence could not be read due to background noise.
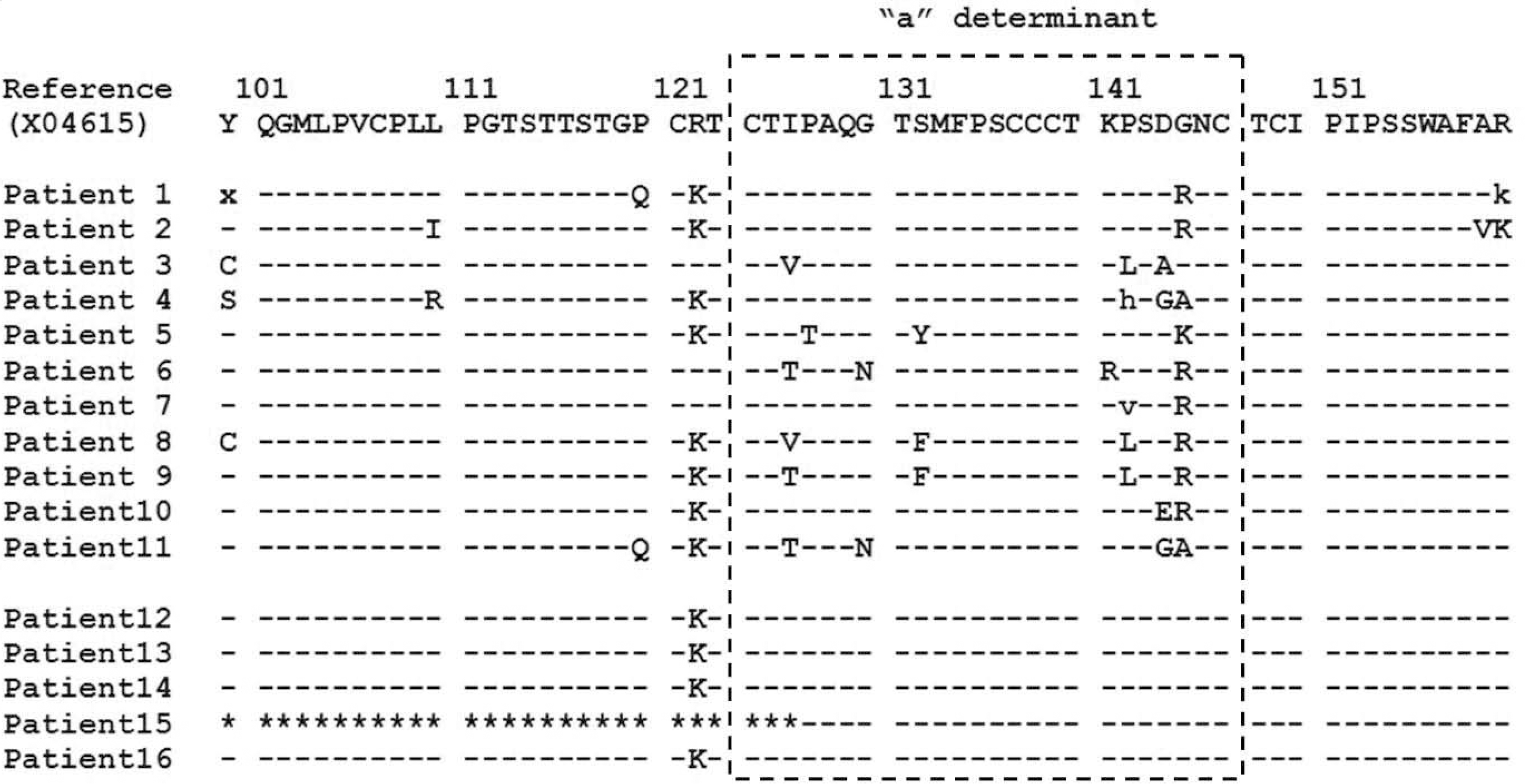
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of 16 patients with HBsAg RIA (−) and HBV DNA (+)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download