Abstract
Methods
The Korean version of the National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire 25 (NEI-VFQ-25) was completed by 105 glaucoma clinic patients including 54 glaucoma group and 56 control group. We compared questionnaire scores and previous performed visual field parameters between a glaucoma group and a control group.
Results
The glaucoma group results were: Mean age: 55.73 ± 15.17 years; mean best corrected visual acuity (BCVA; log MAR) 0.05 ± 0.09 in better eyes and 0.06 ± 0.09 in worse eyes; and mean intraocular pressure (IOP) 15.94 ± 2.93 mm Hg in better eyes and 15.49 ± 3.18 mm Hg in worse eyes. Control group scores were: Mean age: 51.85 ± 11.36 years; mean BCVA (log MAR) 0.04 ± 0.07 in better eyes and 0.06 ± 0.08 in worse eyes; and mean IOP 16.40 ± 2.50 mm Hg in better eyes and 16.13 ± 2.16 mm Hg in worse eyes. Age, BCVA, and IOP were not significantly different between groups, but visual field index (VFI) score and visual function questionnaire (NEI-VFQ-25) total score were significantly lower in the glaucoma group (p < 0.01). Additionally, visual field parameters and QOL had a significant relationship in the glaucoma group, especially in better eyes.
References
2. Armaly MF. Ocular pressure and visual fields. A ten-year follow-up study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969; 81:25–40.
3. The effectiveness of intraocular pressure reduction in the treatment of normal-tension glaucoma. Collaborative Normal-Tension Glaucoma Study Group. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:498–505.
4. Levene RZ. Low tension glaucoma: a critical review and new material. Surv Ophthalmol. 1980; 24:621–64.

5. Perkins ES. The Bedford glaucoma survey. I. Long-term follow-up of borderline cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 1973; 57:179–85.

6. Guedes RA, Guedes VM, Freitas SM, Chaoubah A. Quality of life of glaucoma patients under medical therapy with different prostaglandins. Clin Ophthalmol. 2012; 6:1749–53.
7. Hahm BJ, Shin YW, Shim EJ, et al. Depression and the vision-related quality of life in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 92:650–4.

8. Seo JH, Yu HG, Lee BJ. Assessment of functional vision score and vision-specific quality of life in individuals with retinitis pigmentosa. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2009; 23:164–8.

9. Kim JW, Choi KS, Rhee MR, Lee SJ. Impact of intravitreal bevacizumab injection on life quality in patients with branch retinal vein occlusion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1465–71.

10. Clemons TE, Chew EY, Bressler SB, McBee W. National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire in the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS): AREDS Report No. 10. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:211–7.
11. Klein R, Moss SE, Klein BE, et al. The NEI-VFQ-25 in people with long-term type 1 diabetes mellitus: the Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:733–40.
12. Mangione CM, Lee PP, Pitts J, et al. Psychometric properties of the National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI-VFQ). NEI-VFQ Field Test Investigators. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:1496–504.
13. Mangione CM, Lee PP, Gutierrez PR, et al. Development of the 25-item National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:1050–8.
14. Suzukamo Y, Oshika T, Yuzawa M, et al. Psychometric properties of the 25-item National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI VFQ-25), Japanese version. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2005; 3:65.

15. Lohr KN, Brook RH, Kamberg CJ, et al. Use of medical care in the Rand Health Insurance Experiment. Diagnosis- and service-specific analyses in a randomized controlled trial. Med Care. 1986; 24(9 Suppl):S1–87.
16. McHorney CA, Ware JE Jr, Raczek AE. The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): II. Psychometric and clinical tests of validity in measuring physical and mental health constructs. Med Care. 1993; 31:247–63.
17. Heo JW, Yoon HS, Shin JP, et al. A validation and reliability study of the Korean version of national eye institute visual function questionnaire 25. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:1354–67.

18. Sawada H, Fukuchi T, Abe H. Evaluation of the relationship between quality of vision and the visual function index in Japanese glaucoma patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011; 249:1721–7.

19. Okamoto M, Sugisaki K, Murata H, et al. Impact of better and worse eye damage on quality of life in advanced glaucoma. Sci Rep. 2014; 4:4144.

20. Qiu M, Wang SY, Singh K, Lin SC. Association between visual field defects and quality of life in the United States. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:733–40.
Figure 1.
Negative correlation of age and NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire total scale. (A) Age and total score in glaucoma group (r = −0.279, p < 0.05). (B) Age and total score in control group (r = −0.469, p < 0.01).
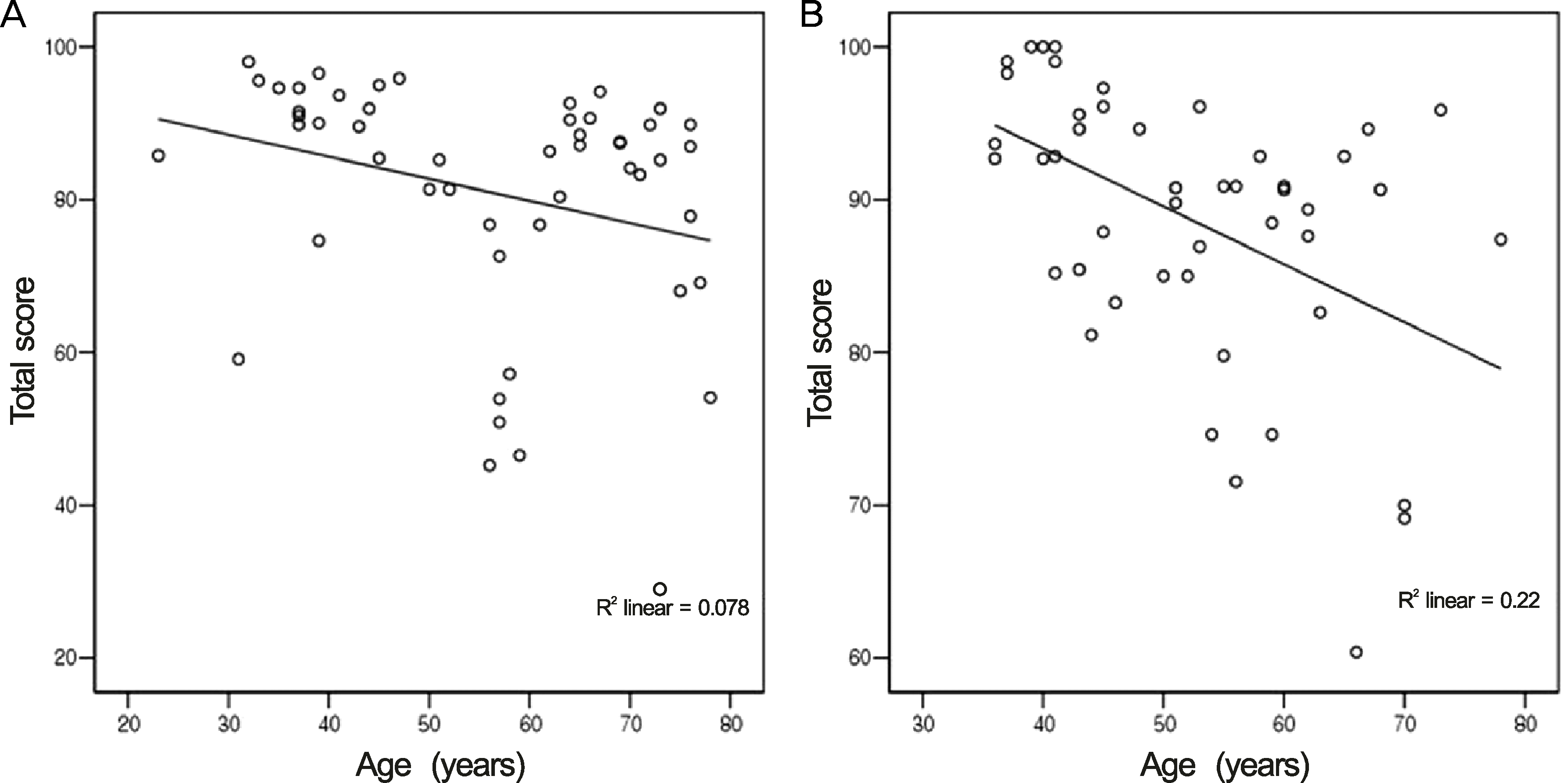
Figure 2.
NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire total scale and visual field index of both eyes in glaucoma group showed significant correlation. (A) Visual field index and total score (r = 0.381, p < 0.01). (B) Mean deviation and total score (r = 0.411, p < 0.01). (C) Pattern standard deviation and total score (r = −0.321, p < 0.05). VFI = visual field index; MD = mean deviation; PSD = pattern standard deviation.
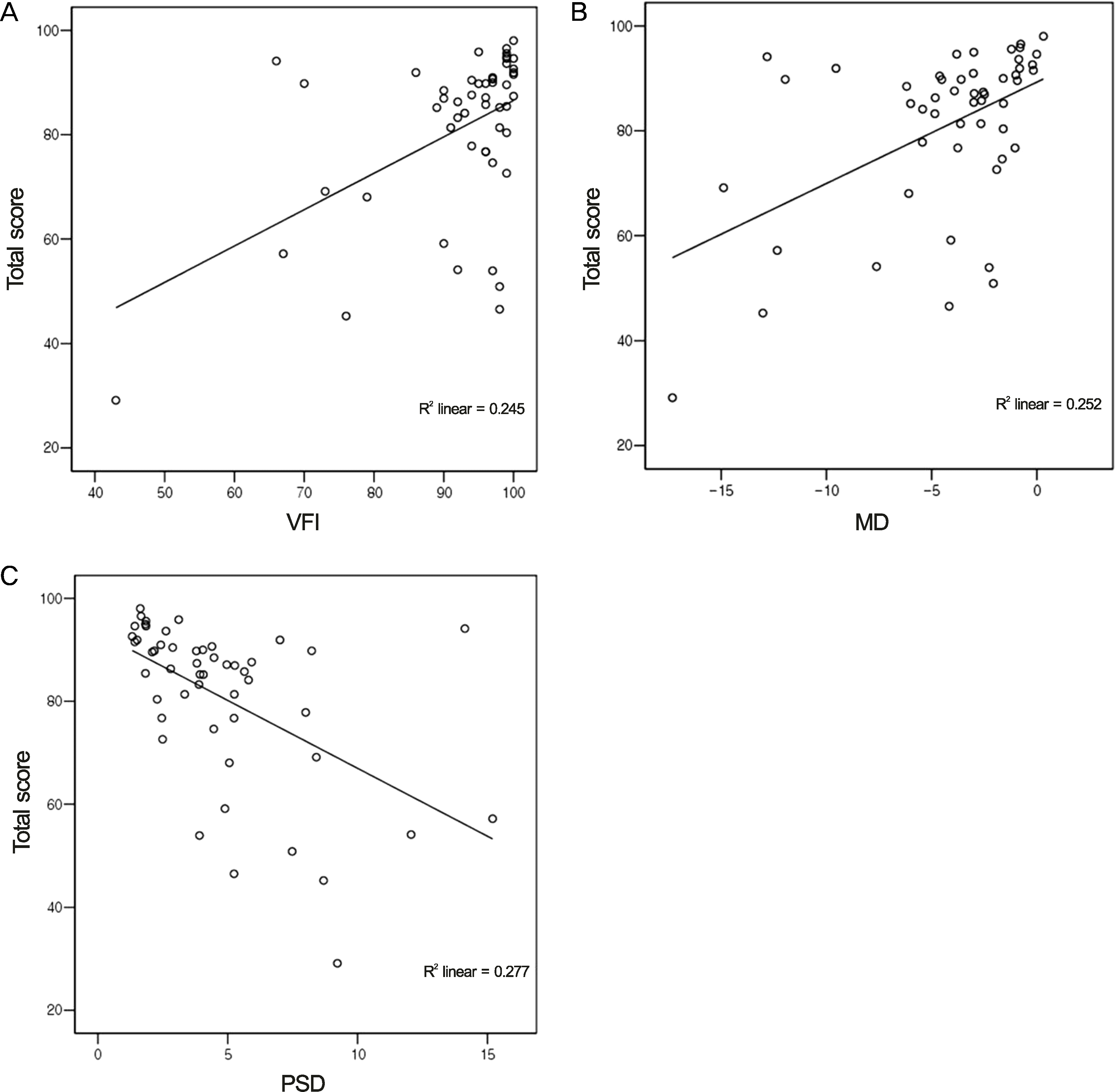
Table 1.
Baseline characteristic of study and control group
| Glaucoma | Control | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 52 | 53 | |
| Age (years) | 55.73 ± 15.17 | 51.85 ± 11.36 | 0.147 |
| Sex (M/F) | 27/25 | 25/28 | 0.630 |
| Mean BCVA (log MAR) | |||
| Better eye | 0.05 ± 0.09 | 0.04 ± 0.07 | 0.449 |
| Worse eye | 0.06 ± 0.09 | 0.06 ± 0.08 | 0.622 |
| Mean IOP | |||
| Better eye | 15.94 ± 2.93 | 16.40 ± 2.50 | 0.407 |
| Worse eye | 15.49 ± 3.18 | 16.13 ± 2.16 | 0.246 |
| HT | 17 (33%) | 9 (17%) | 0.071 |
| DM | 10 (19%) | 7 (13%) | 0.431 |
| CVD | 2 (4%) | 2 (4%) | 0.951 |
| Visual field | |||
| VFI | |||
| Better eye | 92.14 ± 11.17 | 98.52 ± 2.00 | <0.01* |
| Worse eye | 79.27 ± 20.12 | 96.58 ± 3.21 | <0.01* |
| MD | |||
| Better eye | −4.25 ± 4.08 | −1.79 ± 1.33 | <0.01* |
| Worse eye | −8.36 ± 6.44 | −2.74 ± 1.70 | <0.01* |
| PSD | |||
| Better eye | 4.66 ± 3.14 | 2.37 ± 1.32 | <0.01* |
| Worse eye | 7.58 ± 3.93 | 3.75 ± 2.42 | <0.01* |
Table 2.
Comparison of NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire scale between the study group and control group
| VFQ-25 questionnaire scale | Glaucoma group (n = 53) | Control group (n = 54) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| General health | 40.20 ± 24.02 | 53.65 ± 25.78 | 0.008* |
| General vision | 49.41 ± 17.60 | 61.25 ± 19.09 | 0.002* |
| Ocular pain | 81.62 ± 19.74 | 86.72 ± 16.39 | 0.166 |
| Near activities | 81.54 ± 21.56 | 89.67 ± 13.34 | 0.026* |
| Distance activities | 81.70 ± 17.32 | 90.71 ± 12.78 | 0.004* |
| Social functioning | 92.14 ± 12.33 | 96.35 ± 7.72 | 0.121 |
| Mental health | 79.29 ± 24.89 | 90.36 ± 8.05 | 0.004* |
| Role difficulties | 78.92 ± 28.01 | 89.58 ± 17.17 | 0.024* |
| Dependency | 92.48 ± 17.89 | 98.09 ± 5.50 | 0.037* |
| Color vision | 95.10 ± 13.25 | 95.83 ± 10.74 | 0.763 |
| Driving | 87.22 ± 12.14 | 89.42 ± 12.14 | 0.581 |
| Peripheral vision | 89.22 ± 18.20 | 92.19 ± 13.80 | 0.364 |
| Total | 81.07 ± 15.74 | 88.69 ± 8.96 | 0.004* |
Table 3.
Correlations between NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire scale and visual field index in the better eye of glaucoma group
| VFQ-25 questionnaire scale | Mean BCVA (log MAR) | VFI | MD | PSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General health | 0.316 | 0.697 | 0.651 | 0.859 |
| (-0.148) | (0.053) | (0.058) | (-0.024) | |
| General vision | 0.857 | 0.547 | 0.245 | 0.255 |
| (-0.027) | (0.083) | (0.148) | (-0.151) | |
| Ocular pain | 0.838 | 0.568 | 0.800 | 0.055 |
| (-0.028) | (0.073) | (0.030) | (-0.255) | |
| Near activities | 0.692 | 0.022* | 0.015* | 0.008* |
| (-0.065) | (0.320) | (0.311) | (-0.379) | |
| Distance activities | 0.143 | 0.002* | 0.004* | 0.010* |
| (-0.218) | (0.426) | (0.398) | (-0.338) | |
| Social functioning | 0.203 | 0.006* | 0.014* | 0.022* |
| (-0.183) | (0.355) | (0.298) | (-0.291) | |
| Mental health | 0.035* | 0.013* | 0.010* | 0.013* |
| (-0.292) | (0.315) | (0.307) | (-0.307) | |
| Role difficulties | 0.459 | 0.008* | 0.031* | 0.010* |
| (-0.104) | (0.333) | (0.256) | (-0.316) | |
| Dependency | 0.056 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.010* |
| (-0.272) | (0.541) | (0.474) | (-0.326) | |
| Color vision | 0.376 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.034* |
| (-0.129) | (0.604) | (0.459) | (-0.274) | |
| Driving | 0.958 | 0.239 | 0.414 | 0.056 |
| (-0.014) | (0.166) | (0.125) | (-0.290) | |
| Peripheral vision | 0.901 | 0.008* | 0.032* | 0.006* |
| (-0.019) | (0.365) | (0.281) | (-0.367) | |
| Total | 0.171 | 0.005* | 0.006* | 0.002* |
| (-0.202) | (0.368) | (0.338) | (-0.392) |
Table 4.
Correlations between NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire scale and visual field index in the worse eye of glaucoma group
| VFQ-25 questionnaire scale | Mean BCVA (log MAR) | VFI | MD | PSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General health | 0.197 | 0.850 | 0.633 | 0.185 |
| (-0.167) | (0.027) | (0.067) | (-0.202) | |
| General vision | 0.156 | 0.049* | 0.025* | 0.113 |
| (-0.182) | (0.280) | (0.305) | (-0.241) | |
| Ocular pain | 0.833 | 0.414 | 0.212 | 0.335 |
| (-0.026) | (0.109) | (0.161) | (-0.137) | |
| Near activities | 0.142 | 0.048* | 0.058 | 0.362 |
| (-0.208) | (0.311) | (0.288) | (-0.155) | |
| Distance activities | 0.014* | 0.004* | 0.006* | 0.226 |
| (-0.312) | (0.403) | (0.379) | (-0.188) | |
| Social functioning | 0.009* | 0.027* | 0.053 | 0.568 |
| (-0.319) | (0.305) | (0.260) | (-0.086) | |
| Mental health | 0.144 | 0.011* | 0.003* | 0.026* |
| (-0.179) | (0.339) | (0.376) | (-0.319) | |
| Role difficulties | 0.079 | 0.110 | 0.098 | 0.255 |
| (-0.212) | (0.216) | (0.216) | (-0.165) | |
| Dependency | 0.226 | 0.025* | 0.022* | 0.310 |
| (-0.154) | (0.310) | (0.305) | (-0.152) | |
| Color vision | 0.235 | 0.114 | 0.332 | 0.888 |
| (-0.151) | (0.224) | (0.134) | (-0.022) | |
| Driving | 0.900 | 0.972 | 0.732 | 0.615 |
| (-0.019) | (0.008) | (0.075) | (-0.127) | |
| Peripheral vision | 0.261 | 0.038* | 0.127 | 0.914 |
| (-0.151) | (0.308) | (0.220) | (-0.017) | |
| Total | 0.068 | 0.010* | 0.007* | 0.043* |
| (-0.232) | (0.361) | (0.367) | (-0.296) |
Table 5.
Comparison of NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire scale according to hypertension in glaucoma group
| VFQ-25 questionnaire scale | HT (+) (n = 18) | HT (-) (n = 35) | p-value | p-value (adjusted)† |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General health | 29.41 ± 25.36 | 45.59 ± 21.73 | 0.010* | 0.219 |
| General vision | 41.18 ± 13.17 | 53.53 ± 18.24 | 0.020* | 0.239 |
| Ocular pain | 80.15 ± 17.71 | 82.35 ± 20.89 | 0.474 | 0.611 |
| Near activities | 68.14 ± 28.14 | 88.23 ± 13.47 | 0.018* | 0.128 |
| Distance activities | 73.04 ± 20.73 | 86.03 ± 13.72 | 0.021* | 0.277 |
| Social functioning | 90.44 ± 15.01 | 94.48 ± 10.74 | 0.435 | 0.507 |
| Mental health | 71.32 ± 30.46 | 83.09 ± 24.79 | 0.071 | 0.325 |
| Role difficulties | 70.58 ± 32.76 | 83.08 ± 24.78 | 0.178 | 0.582 |
| Dependency | 84.31 ± 26.00 | 96.57 ± 10.28 | 0.005* | 0.339 |
| Color vision | 89.71 ± 19.88 | 97.79 ± 7.19 | 0.053 | 0.908 |
| Driving | 75.01 ± 12.23 | 88.09 ± 12.10 | 0.315 | 0.859 |
| Peripheral vision | 77.94 ± 24.82 | 94.85 ± 10.26 | 0.003* | 0.164 |
| Total | 73.03 ± 19.58 | 85.09 ± 11.81 | 0.140 | 0.228 |
Table 6.
Comparison of NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire scale according to sex in glaucoma group
| VFQ-25 questionnaire scale | Man (n = 28) | Woman (n = 25) | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| General health | 42.59 ± 24.82 | 37.50 ± 23.31 | 0.984 |
| General vision | 48.89 ± 16.01 | 50.01 ± 19.56 | 0.261 |
| Ocular pain | 81.02 ± 23.61 | 82.29 ± 14.71 | 0.846 |
| Near activities | 87.65 ± 18.68 | 74.65 ± 22.85 | 0.231 |
| Distance activities | 84.25 ± 18.24 | 78.82 ± 16.11 | 0.833 |
| Social functioning | 96.29 ± 10.86 | 89.58 ± 13.12 | 0.229 |
| Mental health | 82.17 ± 21.14 | 76.04 ± 28.65 | 0.566 |
| Role difficulties | 81.94 ± 26.25 | 75.52 ± 25.05 | 0.752 |
| Dependency | 94.22 ± 6.93 | 89.15 ± 24.21 | 0.120 |
| Color vision | 97.22 ± 8.01 | 92.71 ± 15.26 | 0.814 |
| Driving | 89.06 ± 10.85 | 79.16 ± 8.33 | 0.157 |
| Peripheral vision | 91.66 ± 18.34 | 86.45 ± 18.02 | 0.923 |
| Total | 84.21 ± 13.37 | 77.54 ± 17.66 | 0.458 |
Table 7.
Comparison of NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire scale according to DM in glaucoma group
| VFQ-25 questionnaire scale | DM (+) (n = 12) | DM (-) (n = 41) | p-value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| General health | 25.00 ± 16.67 | 43.90 ± 24.23 | 0.133 |
| General vision | 46.00 ± 16.46 | 50.24 ± 17.95 | 0.803 |
| Ocular pain | 86.25 ± 19.93 | 80.48 ± 19.77 | 0.410 |
| Near activities | 78.33 ± 23.30 | 82.32 ± 21.34 | 0.287 |
| Distance activities | 79.16 ± 18.53 | 82.31 ± 17.19 | 0.536 |
| Social functioning | 93.75 ± 15.86 | 92.78 ± 11.54 | 0.181 |
| Mental health | 79.37 ± 23.76 | 79.26 ± 25.44 | 0.804 |
| Role difficulties | 76.25 ± 31.57 | 79.57 ± 26.33 | 0.882 |
| Dependency | 87.50 ± 21.93 | 93.69 ± 14.28 | 0.682 |
| Color vision | 87.50 ± 24.29 | 93.95 ± 8.28 | 0.180 |
| Driving | 83.33 ± 9.25 | 87.49 ± 11.52 | 0.848 |
| Peripheral vision | 82.51 ± 26.48 | 89.85 ± 15.56 | 0.717 |
| Total | 78.49 ± 20.06 | 81.70 ± 14.73 | 0.716 |
Table 8.
Comparison of NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire scale according to topical medication in glaucoma group
| VFQ-25 questionnaire scale |
Glaucoma topical medication |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| One eye drop (n = 39) | More than one (n = 14) | p-value* | |
| General health | 41.67 ± 23.88 | 35.42 ± 24.91 | 0.392 |
| General vision | 50.77 ± 18.26 | 45.00 ± 15.08 | 0.278 |
| Ocular pain | 85.90 ± 13.20 | 67.71 ± 29.89 | 0.064 |
| Near activities | 83.12 ± 20.10 | 76.39 ± 26.07 | 0.242 |
| Distance activities | 84.40 ± 14.95 | 72.92 ± 21.94 | 0.122 |
| Social functioning | 94.23 ± 11.05 | 89.58 ± 15.84 | 0.196 |
| Mental health | 82.05 ± 23.44 | 70.31 ± 28.35 | 0.124 |
| Role difficulties | 82.05 ± 25.78 | 68.75 ± 33.50 | 0.126 |
| Dependency | 92.74 ± 19.70 | 91.67 ± 10.66 | 0.799 |
| Color vision | 95.51 ± 13.90 | 93.75 ± 11.31 | 0.585 |
| Driving | 86.81 ± 12.54 | 88.89 ± 12.73 | 0.930 |
| Peripheral vision | 90.38 ± 15.83 | 85.42 ± 24.91 | 0.334 |
| Total | 82.98 ± 15.22 | 74.87 ± 16.47 | 0.089 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download