Abstract
Purpose
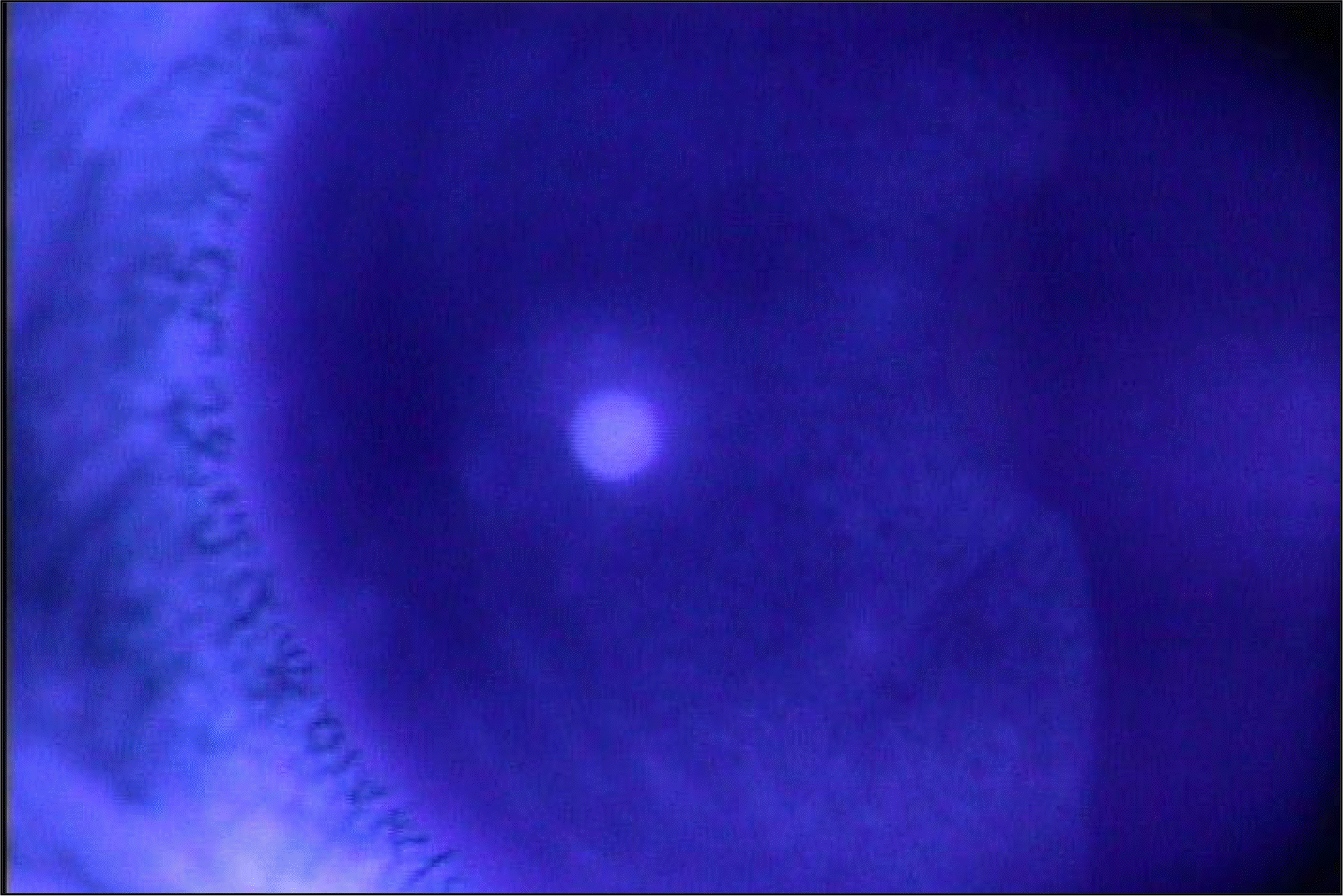
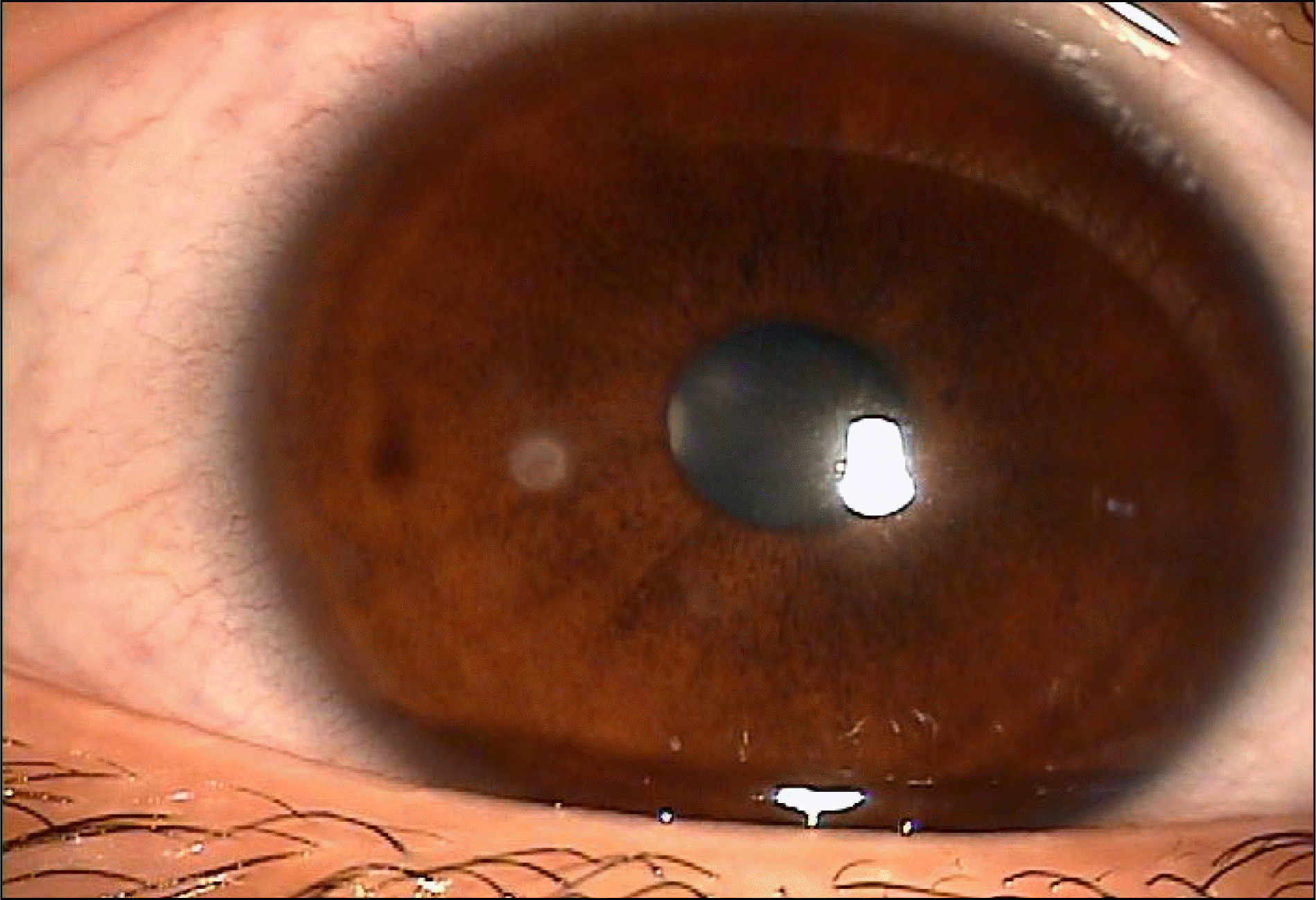
To report a case of corneal ulcer due to Alcaligenes xylosoxidans in a soft contact lens wearer.
Case summary
A 20-year-old female patient presented with a corneal ulcer. The patient had been wearing soft contact lenses over 6 months. The ulcer had a typical appearance, similar to that of immune infiltration due to contact lenses. However, the corneal scraping and culture yielded Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, which is susceptible to ceftazidime and levo-floxacine in the antibiotic susceptibility test. After treatment with topical antibiotics, her eye improved, with only a mild corneal scar remaining.
References
1. Holmes B, Snell JJ, Lapage SP. Strains of Achromobacter xylosoxidans from clinical material. J Clin Pathol. 1977; 30:595–601.

2. Han YS, Chung IY, Park JM. A case of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans endophthalmitis after cataract extraction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:186–9.
3. Oh J-Y, Shin YJ, Wee WR. A case of Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis complicated by Alcaligenes xylosoxidans infection. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:233–4.

4. Hwang JH, Kim MJ, Kweon EY, et al. A case of corneal ulcer by Alcaligenes Faecalis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1414–7.

5. Fiscella R, Noth J. Achromobacter xylosoxidans corneal ulcer in a therapeutic soft contact lens wearer. Cornea. 1989; 8:267–9.

6. Pan TH, Heidemann DG, Dunn SP, et al. Delayed onset and recurrent Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratitis. Cornea. 2000; 19:243–5.

7. Lin A, Driebe WT, Polack P. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratiits post penetrating keratoplasty in a rigid gas permeable lens wearer. CLAO J. 1998; 24:239–41.
8. Huang ZL, Chen YF, Chang SW, et al. Recurrent Alcalgenes xylosoxidans keratitis. Cornea. 2005; 24:489–90.
9. Yabuuchi E, Ohyama A. Achromobacter xylosoxidans from human ear discharge. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971; 15:477–81.
10. Newman PE, Heider P, Waring GO, et al. Corneal ulcer due to Achromobactere xylosoxidans. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984; 68:472–4.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download