Abstract
Purpose:
To evaluate whether upper eyelid blepharoplasty causes eyebrow position change in patients with or without brow ptosis.
Methods:
We analyzed the photographic records of 28 patients 53 eyes with dermatochalasis who had undergone upper eyelid blepharoplasty. Brow-pupil, brow-lid margin, lid margin-pupil, brow-lateral canthus, and brow-medial canthus distances were measured, and then the proportions of medial canthus-nasal alar were taken. Preoperative and postoperative measurements were compared.
Results:
After blepharoplasty, no one in the group without brow ptosis developed new brow ptosis. In the group with brow ptosis, only one patient felt a significant change in brow position after blepharoplasty. In both groups, the distance between the eyebrow and the lid margin decreased by similar amounts. There was no change in the upper eyelid margin position after blepharoplasty.
References
1. McCord CD, Doxanas MT. Browplasty and browpexy: an adjunct to blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 86:248–54.
2. Chrisman BB. Blepharoplasty and browlift with surgical variations in non-white patients. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1986; 12:58–66.

4. Flowers RS, Flowers SS. Diagnosing photographic distortion. Decoding true postoperativecontour after eyelid surgery. Clin Plast Surg. 1993; 20:387–92.
5. Knize DM. An anatomically based study of the mechanism of eyebrow ptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996; 97:1321–33.

8. Fagien S. Eyebrow analysis after blepharoplasty in patients with brow ptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992; 8:210–4.

9. Goldstein SM, Katowitz JA. The male eyebrow: a topographic anatomic analysis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 21:285–91.

12. Karacalar A, Korkmaz A, Kale A, Kopuz C. Compensatory brow asymmetry: anatomic study and clinical experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005; 29:119–23.

13. Starck WJ, Griffin JE Jr, Epker BN. Objective evaluation of the eyelids and eyebrows after blepharoplasty. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996; 54:297–302.

14. Frankel AS, Kamer FM. The effect of Blepharoplasty on eyebrow position. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; 123:393–6.

15. Flowers RS, Caputy GG, Flowers SS. The biomechanics of brow and frontalis function and its effect on blepharoplasty. Clin Plast Surg. 1993; 20:255–68.

16. Lee YJ, Kang IB, Kim JH. The objective change of the eyelid after upper blepharoplasty. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:337–42.
Figure 1.
Illustration of measured parameters for the eyelid and eyebrow. BLCD=brow-lateral canthal distance, BMD=brow-lid margin distance, MPD=lid margin-pupil distance, BPD=brow-pupil distance, BMCD= brow-medial canthal distance, CAD=canthus-nasal alar distance.
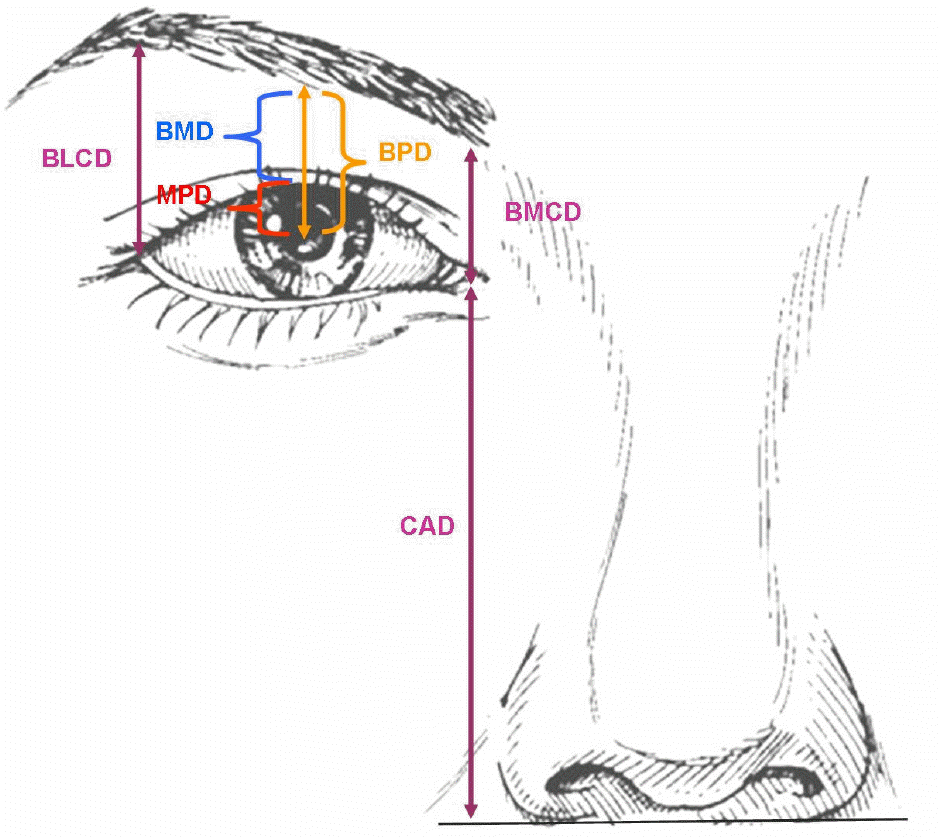
Table 1.
Demographic features of patients
Table 2.
Comparisons of objective changes of measured parameters in patients without brow ptosis
| BPD∗/CAD† | BMD‡/CAD† | MPD§/CAD† | BLCDП/CAD† | BMCD#/CAD† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | 0.426±0.102 | 0.374±0.107 | 0.052±0.020 | 0.435±0.114 | 0.419±0.096 |
| Postoperative | 0.377±0.082 | 0.328±0.094 | 0.049±0.020 | 0.391±0.104 | 0.373±0.073 |
| p-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Table 3.
Comparisons of objective changes of measured parameters in patients with brow ptosis
| BPD∗/CAD† | BMD‡/CAD† | MPD§/CAD† | BLCDП/CAD† | BMCD#/CAD† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | 0.368±0.043 | 0.309±0.048 | 0.049±0.021 | 0.375±0.044 | 0.357±0.081 |
| Postoperative | 0.313±0.043 | 0.258±0.050 | 0.056±0.020 | 0.325±0.066 | 0.311±0.066 |
| p-value | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.26 | <0.01 | <0.01 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download