Abstract
Purpose
To study the use of acellular dermal allografts for the reconstruction of contracted anophthalmic sockets.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was performed on 12 patients with contracted sockets who underwent reconstructive surgery using acellular dermal allografts from 2002 to 2006.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 44.4 years. The mean duration of conjunctival sac contracture after removal of the eyeball was 21.4 years. In 4 patients, acellular dermal allografts were used as spacer grafts to elevate the eyelids, and in 8 patients the allografts were used as a conjunctival grafting material. All patients were able to wear ocular prostheses comfortably 2.2 months after surgery with acceptable cosmesis. There were no serious complications, such as infections or graft rejections during follow-up period.
References
1. Soll DB. Reconstruction of a contracted socket. The use of an expandable silicone tire. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969; 82:218–9.
2. Guyuron B. Retroauricular island flap for eye socket reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985; 76:527–33.

3. Molgat YM, Hurtwitz JJ, Webb MC. Buccal mucous membranefat graft in the management of the contracted socket. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 9:267–72.

4. Suh IS, Yang YM, Oh SJ. Conjunctival cul-de-sac reconstruction with radial forearm free flap in anophthalmic orbit syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 107:914–9.

5. Lee AC, Fedorovich I, Heinz GW, Kikkawa DO. Socket reconstruction with combined mucous membrane and hard palate mucosal grafts. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2002; 33:463–8.

6. Sullivan SA, Dailey RA. Graft contraction: a comparison of acellular dermis versus hard palate mucosa in lower eyelid surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 19:14–24.
7. Lee NY, Choi WC, Yang SW. Anophthalmic conjunctival sac reconstruction using acellular dermal allograft. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:703–8.
8. Ji JY, Kim YD. Acellular dermal allograft for the correction of eyelid retraction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1–9.
9. Rubin PA, Fay AM, Remulla HD, Maus M. Ophthalmic plastic applications of acellular dermal allografts. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:2091–7.

10. Shorr N, Perry JD, Goldberg RA, et al. The safety and applications of acellular human dermal allograft in ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive surgery: a preliminary report. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 16:223–30.
11. Aldave AJ, Maus M, Rubin PA. Advances in the management of lower eyelid retraction. Facial Plast Surg. 1999; 15:213–24.

12. Kronish JW, Gonnering RS, Dortzbach RK, et al. The pathophysiology of the anophthalmic socket: Part I. Analysis of orbital blood flow. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 6:77–87.

13. Kronish JW, Gonnering RS, Dortzbach RK, et al. The pathophysiology of the anophthalmic socket: Part II. Analysis of orbital fat. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 6:88–95.

14. Kaltreider SA, Wallow IH, Gonnering RS, Dortzbach RK. The anatomy and histology of the anophthalmic socket: Is the myofibroblast present? Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1987; 3:207–30.
15. Wainwright DJ. Use of an acellular allograft dermal matrix (AlloDerm) in the management of full-thickness burns. Burns. 1995; 21:243–8.

16. Wainwright D, Madden M, Luterman A, et al. Clinical evaluation of an acellular allograft dermal matrix in full-thickness burns. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1996; 17:124–36.

17. Terino EO. Alloderm acellular dermal graft: applications in aesthestic soft-tissue augmentation. Clin Plast Surg. 2001; 28:83–99.
18. Tobin HA, Karas ND. Lip augmentation using an alloderm graft. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998; 56:722–7.

19. Fay AM, Pieroth L, Rubin PA. An animal model of lower eyelid spacer grafting with acellular dermis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 17:270–5.

20. Sclafani AP, Romo T 3rd, Jacono AA, et al. Evaluation of acellular dermal graft (AlloDerm) sheet for soft tissue augmentation: a 1 year follow-up of clinical observations and histological findings. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2001; 3:101–3.
21. Livesey SA, Herndon DN, Hollyoak MA, et al. Transplanted acellular allograft dermal matrix. Potential as a template for the reconstruction of viable dermis. Transplantation. 1995; 60:1–9.
Figure 1.
The correction of contracted socket. (A) As a tarsal substitute to elevate the eyelid. (B) As a conjunctival grafting material.
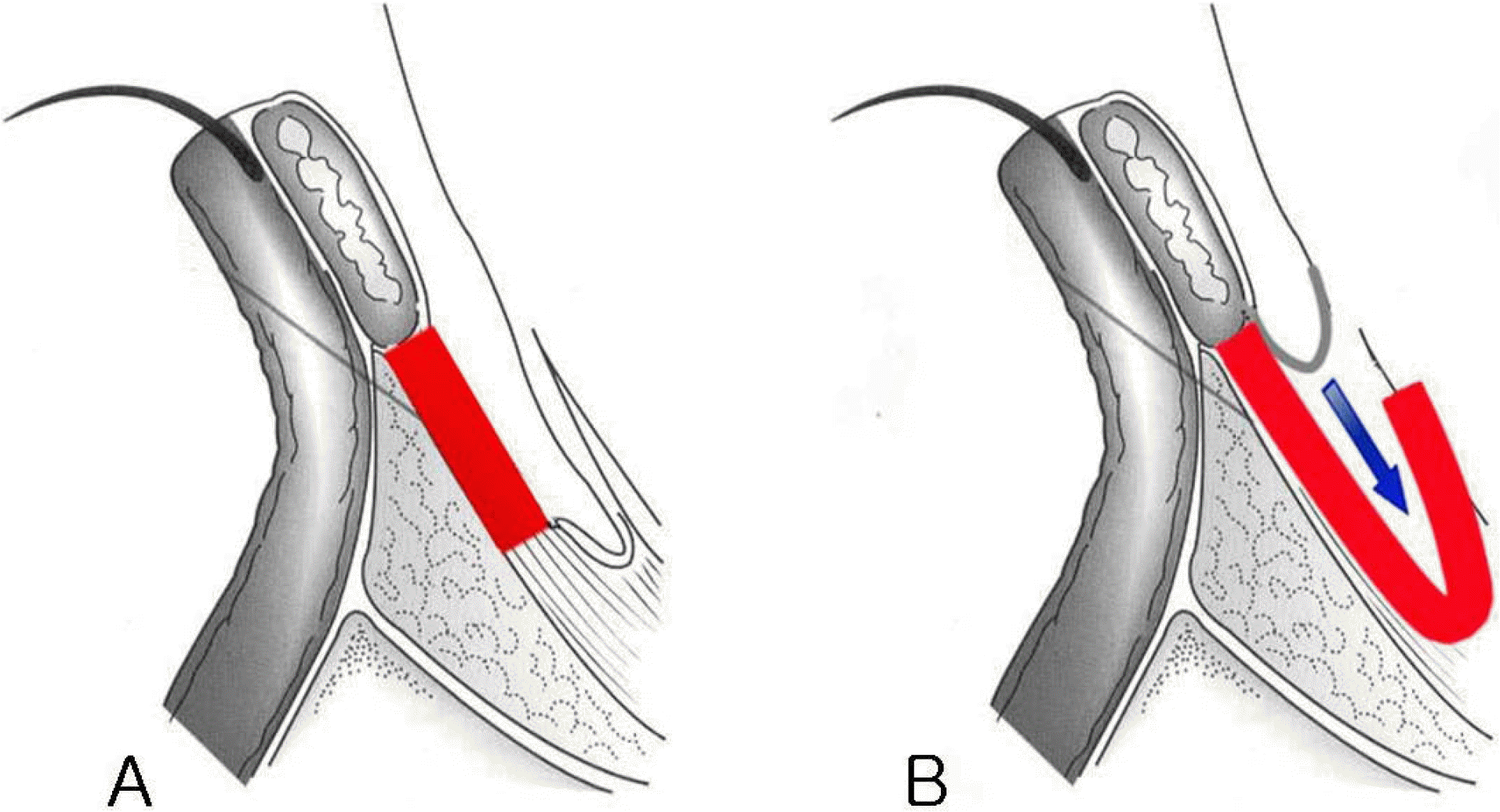
Figure 2.
Case 2. (A) Preoperative photograph showed severe socket contracture. (B) Postoperative photograph taken 1 month after the operation. We performed upper and lower conjunctival sac reconstruction using acellular dermal graft as a conjunctival grafting material. (C), (D) Postoperative photograph taken 4 months after the operation. He was able to wear the prosthesis with good cosmesis.
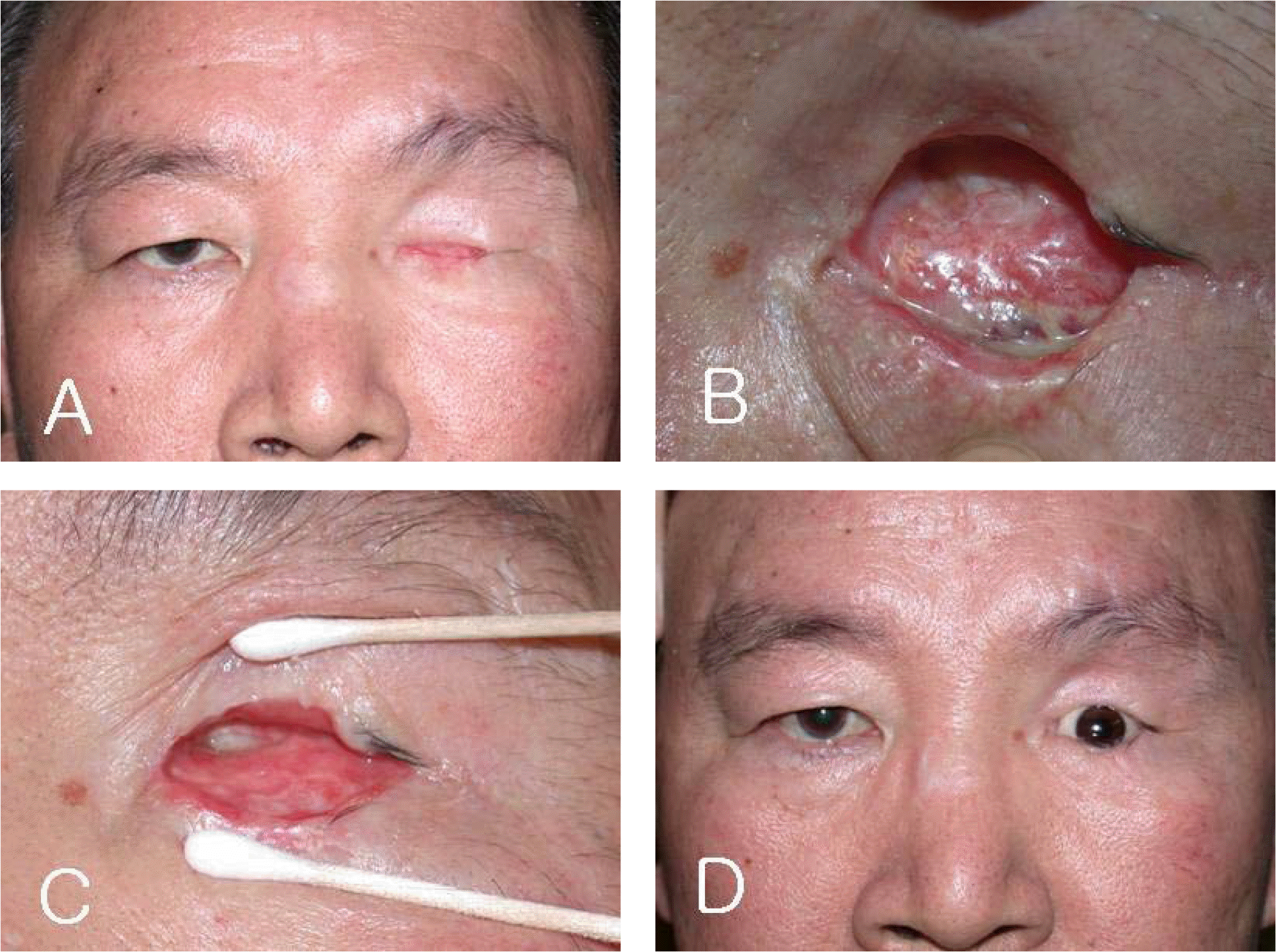
Figure 3.
Case 7. (A) Preoperative photograph showed inferior dystopia, lower lid entropion, and retraction in a 50-year-old woman with anophthalmos. (B) She underwent the lower eyelid reconstruction with acellular dermal graft to elevate the eyelid. Postoperative photograph 8 months after the operation. Good lower eyelid position was achieved.
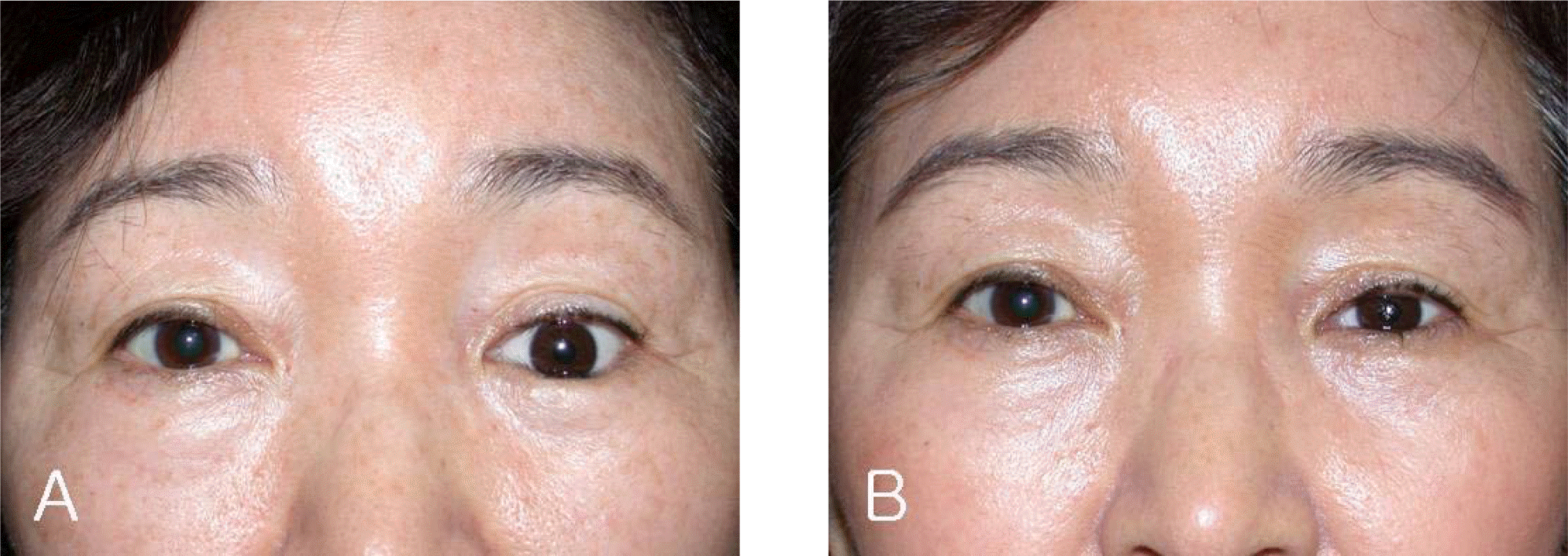
Table 1.
Summary of patients
| No. | Sex/ Age | Type of surgery | Cause of removal | Removal time‡ | Time to contraction after removal | Degree of contracture | Eyelid§ | Purpose of graftΠ | Type of Graft# | Follow up (months) | Prosthesis (months) | Complication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M/23 | Enu* | Retinoblastoma | 6 | 15 yrs | Moderate | L | C | A | 2 | Immediate | None |
| 2 | M/59 | Enu | Trauma | 24 | Unknown | Severe | U/L | C | A | 35 | 2 | None |
| 3 | M/39 | Evi† | Trauma | 26 | 11 yrs | Moderate | L | C | A | 1 | Immediate | None |
| 4 | F/30 | Evi | Trauma | 8 | 19 yrs | Mild | L | T | A | 5 | 1 | None |
| 5 | F/54 | Evi | Trauma | 53 | 6 months | Moderate | L | C | A | 27 | 7 | Delay of reepithelization |
| 6 | M/28 | Enu | Trauma | 7 | 16 yrs | Moderate | L | C | A | 7 | 1.5 | None |
| 7 | F/59 | Enu | Unknown | 3 | 54 yrs | Mild | L | T | A | 40 | 5 | Inflammation |
| 8 | M/70 | Enu | Unknown | 10 | 59 yrs | Moderate | L | C | S | 14 | 1.5 | None |
| 9 | M/22 | Evi | Trauma | 20 | 8 months | Mild | L | T | S | 10 | 3 | None |
| 10 | M/41 | Enu | Trauma | 24 | 3 yrs | Moderate | U/L | C | S | 6 | 2 | Inflammation |
| 11 | F/64 | Evi | Unknown | 6 | 54 yrs | Moderate | L | C | S | 6 | 2 | Inflammation |
| 12 | F/44 | Evi | Trauma | 23 | 3 yrs | Moderate | L | T | S | 10 | 1 | None |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download