Abstract
Methods
We reviewed retrospectively medical records of patients having dysphagia following stroke in Seoul National University hospital from April 2002 through Dec 2009. A total of 578 patients (male and female, 331 and 247) were included. The following parameters were recorded and analyzed: patient's sex, age, type of stroke, onset of dysphagia, location of lesion and the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association National Outcome Measurement System Swallowing Scale (ASHA NOMS). Using Binary logistic regression and multiple regression analysis, the relationship between dysphagia severity and other factors were analyzed.
Results
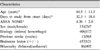
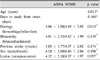
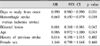
Their average duration between onset of stroke and the date of videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) was 32.3 ± 18.4 days. Patients with hemorrhagic stroke (172 patients, ASHA 4.06 ± 1.98) showed poorer swallowing function than those with ischemic stroke (406 patients, ASHA 4.49 ± 2.02, p=0.013). Binary logistic regression analysis showed that patients who had longer duration from onset to the first study, hemorrhagic stroke, bilateral lesion and older age were at higher risk for dysphagia requiring non-oral supplements (p=0.031, 0.039, 0.042, and 0.043, respectively). Multiple regression analysis revealed that longer duration from onset to study, older age and hemorrhagic stroke were associated with the lower ASHA NOMS (p=0.006, 0.009 and 0.021, respectively). Bilateral lesion, sex, history of previous stroke and involvement of the brainstem, however, were not significant factors.
Figures and Tables
Table 2
American Speech-Language Hearing Association National Outcomes Measurements System Swallowing Scale

References
1. National Health Insurance Coporation Korea. 2000 national health insurance statistical yearbook. 2001. Seoul: National Health Coporation Korea;248–824.
2. Meng NH, Wang TG, Lien IN. Dysphagia in patients with brainstem stroke: incidence and outcome. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2000. 79:170–175.
3. Smithard DG, O Neill PA, England RE, Park CL, Wyatt R, Martin DF, Morris J. The natural history of dysphagia following a stroke. Dysphagia. 1997. 12:188–193.
4. McHorney CA, Robbins J, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, Bricker DE. The SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcomes tool for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults: III. Documentation of reliability and validity. Dysphagia. 2002. 17:97–114.
5. Roth EJ. Medical complications encountered in stroke rehabilitation. Phys Med Rehabil Clin North Am. 1991. 2:563–578.
6. Trapl M, Enderle P, Nowotny M, Teuschl Y, Matz K, Dachenhausen A, Brainin M. Dysphagia bedside screening for acute-stroke patients: the Gugging Swallowing Screen. Stroke. 2007. 38:2948–2952.
7. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. The clinical functional scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Korean J Stroke. 2001. 3:153–157.
8. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. Quantifying swallowing function after stroke: a functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001. 82:677–682.
9. Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 1998. San Diego: College Hill Press;168–180.
10. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. National Outcomes Measurement System (NOMS): Adult Speech-Language Pathology User's Guide. 2003. Rockville MD: American Speech-Language-Hearing Association;17.
11. Song KI, Choi JS. Clinical data analysis by SPSS 15: a practical guide for clinicians. 2008. Seoul: Hannarae Publishing Co.;174.
12. Spencer FA, Allegrone J, Goldberg RJ, Gore JM, Fox KA, Granger CB, Mehta RH, Brieger D. Association of statin therapy with outcomes of acute coronary syndromes: the GRACE study. Ann Intern Med. 2004. 140:857–866.
13. Sellars C, Bowie L, Bagg J, Sweeney MP, Miller H, Tilston J, Langhorne P, Stott DJ. Risk factors for chest infection in acute stroke: a prospective cohort study. Stroke. 2007. 38:2284–2291.
14. Falsetti P, Acciai C, Palilla R, Bosi M, Carpinteri F, Zingarelli A, Pedace C, Lenzi L. Oropharyngeal dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and clinical predictors in patients admitted to a neurorehabilitation unit. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009. 18:329–335.
15. Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 1998. San Diego: College Hill Press;359–364.
16. Paik NJ, Kim IS, Kim JH, Oh BM, Han TR. Clinical Validity of the functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005. 29:43–49.
17. Jung SH, Lee KJ, Hong JB, Han TR. Validation of clinical dysphagia scale: based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005. 29:343–350.
18. Guyomard V, Fulcher RA, Redmayne O, Metcalf AK, Potter JF, Myint PK. Effect of dysphasia and dysphagia on inpatient mortality and hospital length of stay: a database study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009. 57:2101–2106.
19. Mann G, Hankey GJ, Cameron D. Swallowing function after stroke: prognosis and prognostic factors at 6 months. Stroke. 1999. 30:744–748.
20. Horner J, Buoyer FG, Alberts MJ, Helms MJ. Dysphagia following brain-stem stroke: Clinical correlates and outcome. Arch Neurol. 1991. 48:1170–1173.
21. Kumar S, Langmore S, Goddeau RP Jr, Alhazzani A, Selim M, Caplan LR, Zhu L, Safdar A, Wagner C, Frayne C, Searls DE, Schlaug G. Predictors of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in patients with severe dysphagia from an acute-subacute hemispheric infarction. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010. 09. 18. [Epub ahead of print].




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download