Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
(A) A 52-year-old male who had open femoral fracture and unstable pelvic ring injury was managed with temporary external fixation.
(B) After patient's condition was optimized, conversion to internal fixation using intramedullary nail was performed for femoral fracture.
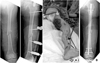
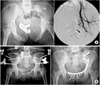
Fig. 2
(A) A 43-year-old female was sustaind from hemodynamically unstable pelvic ring injury. Angiography and embolization was performed as primary treatment for hemorrhage control (arrow).
(B) Pelvic external fixation was carried out for provisional fixation of unstable pelvic ring injury. After patient's condition was optimized, convertsion to internal fixation was performed.
References
1. Agolini SF, Shah K, Jaffe J, Newcomb J, Rhodes M, Reed JF 3rd. Arterial embolization is a rapid and effective technique for controlling pelvic fracture hemorrhage. J Trauma. 1997; 43:395–399.

2. Bone LB, Johnson KD, Weigelt J, Scheinberg R. Early versus delayed stabilization of femoral fractures. A prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:336–340.

3. Bosse MJ, MacKenzie EJ, Riemer BL, et al. Adult respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, and mortality following thoracic injury and a femoral fracture treated either with intramedullary nailing with reaming or with a plate. A comparative study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79:799–809.

4. Chang JD, Seo YJ, Choi YH. Problems of anterior external fixation in unstable pelvic ring injury. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005; 18:394–398.

5. Cook RE, Keating JF, Gillespie I. The role of angiography in the management of haemorrhage from major fractures of the pelvis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:178–182.

6. Copeland CE, Mitchell KA, Brumback RJ, Gens DR, Burgess AR. Mortality in patients with bilateral femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1998; 12:315–319.

7. Copes WS, Champion HR, Sacco WJ, Lawnick MM, Keast SL, Bain LW. The Injury Severity Score revisited. J Trauma. 1988; 28:69–77.

8. Cothren CC, Osborn PM, Moore EE, Morgan SJ, Johnson JL, Smith WR. Preperitonal pelvic packing for hemodynamically unstable pelvic fractures: a paradigm shift. J Trauma. 2007; 62:834–839.

9. Crowl AC, Young JS, Kahler DM, Claridge JA, Chrzanowski DS, Pomphrey M. Occult hypoperfusion is associated with increased morbidity in patients undergoing early femur fracture fixation. J Trauma. 2000; 48:260–267.

10. Demetriades D, Murray J, Charalambides K, et al. Trauma fatalities: time and location of hospital deaths. J Am Coll Surg. 2004; 198:20–26.
11. Ertel W, Keel M, Bonaccio M, et al. Release of anti-inflammatory mediators after mechanical trauma correlates with severity of injury and clinical outcome. J Trauma. 1995; 39:879–885.

12. Ganz R, Krushell RJ, Jakob RP, Küffer J. The antishock pelvic clamp. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; 267:71–78.

13. Gardner MJ, Nork SE. Stabilization of unstable pelvic fractures with supraacetabular compression external fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21:269–273.

14. Ghaemmaghami V, Sperry J, Gunst M, et al. Effects of early use of external pelvic compression on transfusion requirements and mortality in pelvic fractures. Am J Surg. 2007; 194:720–723.

15. Giannoudis PV, Pape HC. Damage control orthopaedics in unstable pelvic ring injuries. Injury. 2004; 35:671–677.

16. Giannoudis PV, Smith RM, Bellamy MC, Morrison JF, Dickson RA, Guillou PJ. Stimulation of the inflammatory system by reamed and unreamed nailing of femoral fractures. An analysis of the second hit. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81:356–361.
17. Hamill J, Holden A, Paice R, Civil I. Pelvic fracture pattern predicts pelvic arterial haemorrhage. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000; 70:338–343.

18. Harwood PJ, Giannoudis PV, van Griensven M, Krettek C, Pape HC. Alterations in the systemic inflammatory response after early total care and damage control procedures for femoral shaft fracture in severely injured patients. J Trauma. 2005; 58:446–452.

19. Hildebrand F, Giannoudis P, van Griensven M, et al. Secondary effects of femoral instrumentation on pulmonary physiology in a standardised sheep model: what is the effect of lung contusion and reaming? Injury. 2005; 36:544–555.

20. Hoch RC, Rodriguez R, Manning T, et al. Effects of accidental trauma on cytokine and endotoxin production. Crit Care Med. 1993; 21:839–845.

22. Kim HS, Oh CW, Kim PT, et al. Crescent fracture-dislocation of sacroiliac Joint: affecting factors of operative results. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009; 22:71–78.

23. Lindahl J, Hirvensalo E, Böstman O, Santavirta S. Failure of reduction with an external fixator in the management of injuries of the pelvic ring. Long-term evaluation of 110 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81:955–962.
24. Maekawa K, Futami S, Nishida M, et al. Effects of trauma and sepsis on soluble L-selectin and cell surface expression of L-selectin and CD11b. J Trauma. 1998; 44:460–468.

25. Pape HC, Giannoudis PV, Krettek C, Trentz O. Timing of fixation of major fractures in blunt polytrauma: role of conventional indicators in clinical decision making. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:551–562.
26. Pape HC, Hildebrand F, Pertschy S, et al. Changes in the management of femoral shaft fractures in polytrauma patients: from early total care to damage control orthopedic surgery. J Trauma. 2002; 53:452–461.

27. Pape H, Stalp M, v Griensven M, Weinberg A, Dahlweit M, Tscherne H. Optimal timing for secondary surgery in polytrauma patients: an evaluation of 4,314 serious-injury cases. Chirurg. 1999; 70:1287–1293.

28. Parameswaran AD, Roberts CS, Seligson D, Voor M. Pin tract infection with contemporary external fixation: how much of a problem? J Orthop Trauma. 2003; 17:503–507.

29. Poelstra KA, Kahler DM. Supra-acetabular placement of external fixator pins: a safe and expedient method of providing the injured pelvis with stability. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2005; 34:148–151.
30. Rotondo MF, Schwab CW, McGonigal MD, et al. 'Damage control': an approach for improved survival in exsanguinating penetrating abdominal injury. J Trauma. 1993; 35:375–382.
31. Simpson T, Krieg JC, Heuer F, Bottlang M. Stabilization of pelvic ring disruptions with a circumferential sheet. J Trauma. 2002; 52:158–161.

32. Tscherne H, Pohlemann T, Gänsslen A, Hüfner T, Pape HC. Crush injuries of the pelvis. Eur J Surg. 2000; 166:276–282.

33. Tscherne H, Regel G, Pape HC, Pohlemann T, Krettek C. Internal fixation of multiple fractures in patients with polytrauma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 347:62–78.

34. Tucker MC, Nork SE, Simonian PT, Routt ML Jr. Simple anterior pelvic external fixation. J Trauma. 2000; 49:989–994.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download